PIXI Basics

Architecture
PixiJS
- Created by Mat Groves in 2013
- v1.0 released in 2013
- v2.0 released in 2014
- v3.0 released in 2015, multitude of improvements
- v4.0 released in 2016, over 100 plugins
- v5.0 released in 2019, brand-new core
- 11 contributors as of 2019
- production build: 346 kB of size
- since v5.0, many packages are deprecated. See the comments in pixi.js.d.ts
- Main page
- Github
- Documentation
- Examples
PixiJS plugins
- pixi-filters - collection of custom display filters
- pixi-compressed-textures - compressed textures for retina displays
- pixi-ui - simple user interface (still WIP)
- pixi-particles - advanced particle system with an editor
- pixi-sound - WebAudio API playback library
- pixi-viewport - highly configurable camera viewport
- PixiTweener - simple tweener for animations
- pixi5-dragonbones - plugin for dragonbone animations
- pixi5-svg - svg support
- pixi-after-effects - support for After-Effects animations
- pixi-inspector - Chrome DevTools for inspecting scene
- SpritesheetGenerator - spritesheet generator
Namespaces
- only a subset, there are over 500 classes
Namesapces
systems
- individual components of the rendering pipeline
resources
- resources used by BaseTexture to handle different media types
interaction
- handling of input events (keyboard, mouse, touch)
prepare
- asynchronous preparation of the rendering pipeline
extract
- render-specific functions for exporting content
settings
- customizable globals (default resolution, framerate,...)
utils
- generalized utilities
filters
- WebGL-only display filters
Classes
Application
- PIXIJs entry class, should be extended
Runner
- alternative to signals, good for dispatching messages to many objects every frame
State
- WebGL state
Transform
- transformation entity
Ticker
- update loop
Loader
- resource loader
Shader
- helper class for GPU shaders
Spritesheet
- utility class for maintaining reference to a collection of textures
Display entities
Display entities
EventEmitter
- high-performance event emitter, similar to the default NodeJS emitter
DisplayObject
- base class of all renderable objects
Container
- a collection of displayable objects
Mesh
- base mesh for rendering any WebGL visuals
Sprite
- base class of all textured objects
Graphics
- class for drawing primitive shapes (lines, circles, rectangles)
ParticleContainer
- very fast version of the Container for drawing lots of sprites
BitmapText
- very fast bitmap text renderer (textures are preloaded)
Display entities
Renderer
- class that draws the scene onto a WebGL canvas
BaseTexture
- wrapper for texture images
BaseRenderTexture
- special texture that allows any object to be rendered to it
CubeTexture
- image/canvas/video/svg texture
Texture
- BaseTexture with metadata
RenderTexture
- RenderTexture with metadata
Display object
Members
- alpha, angle, buttonMode, cursor, filters, hitArea, interactive, localTransform, name, parent, pivot, position, renderable, rotation, scale, skew, transform, visible, worldAlpha, worldTransform, worldVisible, x,y, zIndex
Methods
- destroy, getBounds, getGlobalPosition, getLocalBounds, render, setParent, setTransform, toGlobal, toLocal, updateTransform
Events
- added, click, mousedown, mousemove, mouseout, mouseover, mouseup, removed, tap, touchcancel, touchend, touchmove, touchstart
Setup
Basic application
import * as PIXI from "pixi.js";
export default class MyPixiApp extends PIXI.Application {
constructor(view: HTMLCanvasElement) {
super({ view });
this.ticker.add(deltaTime => this.update(deltaTime));
}
update(deltaTime: number) {
// game loop
}
}
Basic application
- it's better to create a new class and extend PIXI.Application
- the only mandatory attribute for the super class is the canvas entity
- other attributes:
autoStart: boolean, // automatically starts the game loop
width: number, // width of the canvas element (in px)
height: number, // height of the canvas element (in px)
view: HTMLCanvasElement, // link to the canvas
transparent: boolean, // if true, the canvas will be transparent
autoDensity: boolean, // whether CSS dimensions should be resized to screen dim.
antialias: boolean, // sets anti-aliasing
preserveDrawingBuffer: boolean, // if true, preserves stencil buffer
resolution: number, // global scale of the screen (default is 1)
forceCanvas: boolean, // prevents selection of WebGL
backgroundColor: number, // background color of the canvas
clearBeforeRender: boolean, // if true, clears the canvas before next render cycle
forceFXAA: boolean, // forces FXAA anti-aliasing
powerPreference: string, // WebGL parameter for devices with more than one GPU
sharedTicker: boolean, // if true, uses global ticker for updates
sharedLoader: boolean, // if true, uses global loader
resizeTo: Window | HTMLElement, // resizes to a custom HTML element
Examples
- transparent = false
- antialias = false
- resolution = 1
- transparent = false
- antialias = true
- resolution = 1
- transparent = true
- antialias = true
- resolution = 0.2
Ticker
- PixiJS game loop
let ticker = this.ticker;
// prevents autostart
ticker.autoStart = false;
// stops the ticker
ticker.stop();
// starts the ticker if autoStart is false
ticker.start();
=============================
// alternative: manual update
ticker.autoStart = false;
ticker.stop();
let myUpdateLoop =(time) => {
ticker.update(time);
this.renderer.render(this.stage);
requestAnimationFrame(myUpdateLoop);
}
myUpdateLoop(performance.now());
Loader
- responsible for asynchronous loading of assets (fonts, images, sounds, spritesheets)
let loader = this.loader;
// Chainable `add` to enqueue a resource
loader.add('mySprite', 'data/sprite.png') // first parameter is an alias
.add('spritesheet', 'assets/spritesheet.json')
.add('bitmapFont', 'assets/score.fnt');
// loading is asynchronous !!
loader.load((loader, resources) => {
// init the rest of the game and run the ticker
});
// loader events
loader.onProgress.add(() => {}); // called once per loaded/errored file
loader.onError.add(() => {}); // called once per errored file
loader.onLoad.add(() => {}); // called once per loaded file
loader.onComplete.add(() => {}); // called once when the queued resources all load
Positioning
Positioning
- position, rotation, scale, zIndex
- rotation - rotation in radians
- pivot - origin of the object in px (rotation is always around the origin
- anchor - relative origin of the object (only for Sprites
- the scale of the parent affects the units of its children (common behavior of all gfx libraries)
- pivot is not affected by the scale, it always takes into account the size of the object in px
- stage is the root element of the scene graph
- getBounds() - retrieves the bounds of the object, can be used to check where the object is
- toGlobal() - calculates the global position
- toLocal() - calculates the local position relative to another point
Positioning
- positioning of a single element
Positioning
- rotation is around the origin/pivot, which is by default in the top-left corner
Positioning
- pivot also affects the offset of the location of the object
Positioning
- having the pivot in the center, we can rotate the object around its center
Positioning
- the scale of parent objects affects the units of their children
Positioning
- same values, yet the squares are children of the root element
Positioning
- the green and the blue square are children of the red square
Resiting and aspect ratio
Resizing and aspect ratio
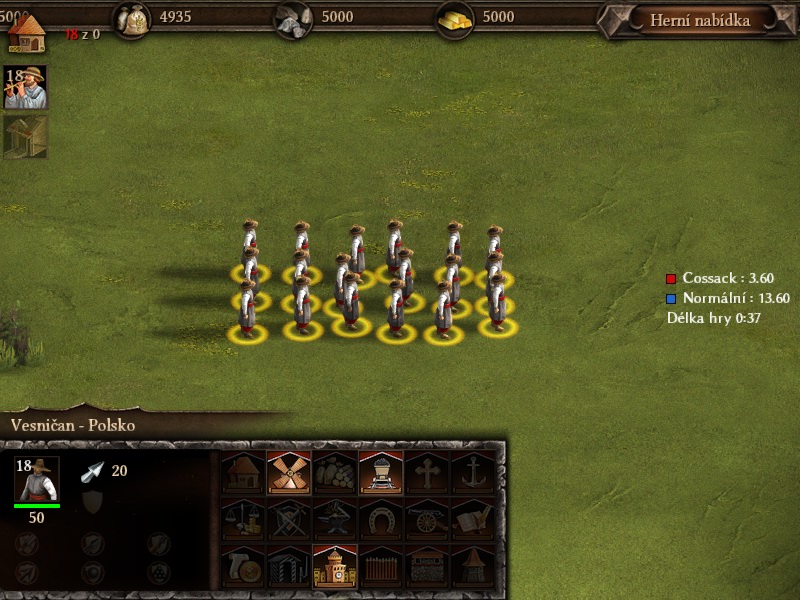
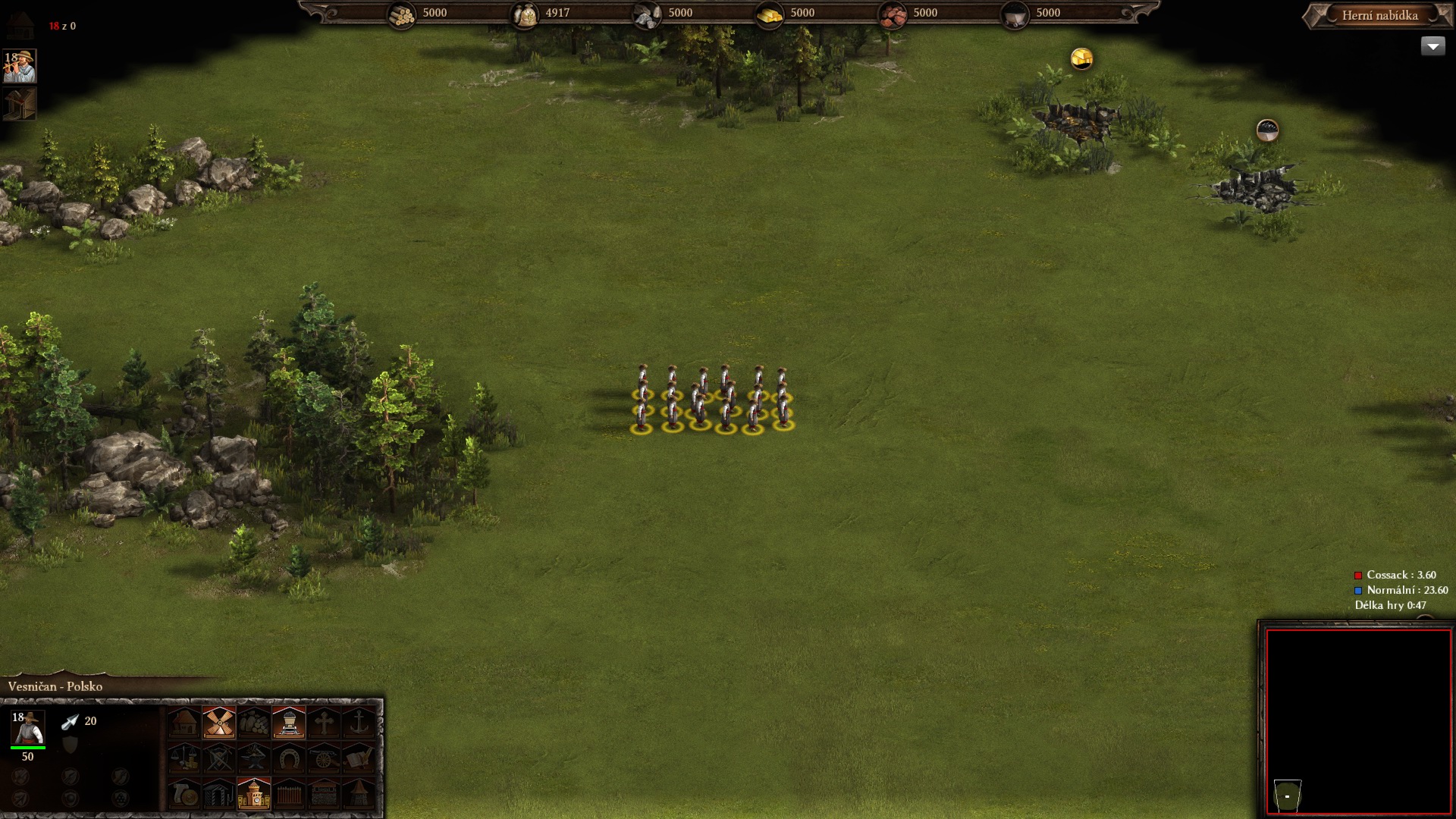
Cossacks 3, 800x600 (4:3)
Cossacks 3, 1920x1080 (16:9)
Resizing and aspect ratio
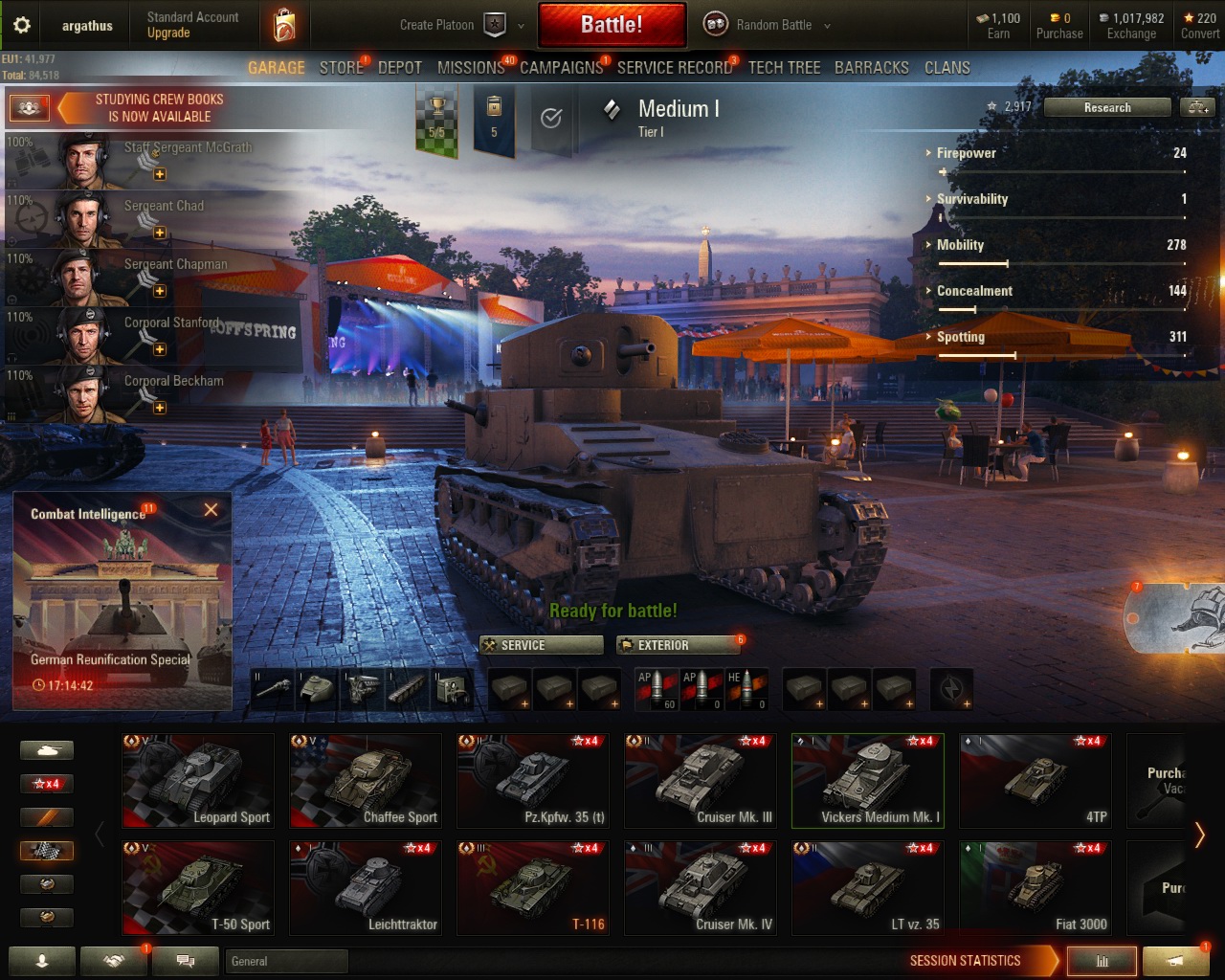
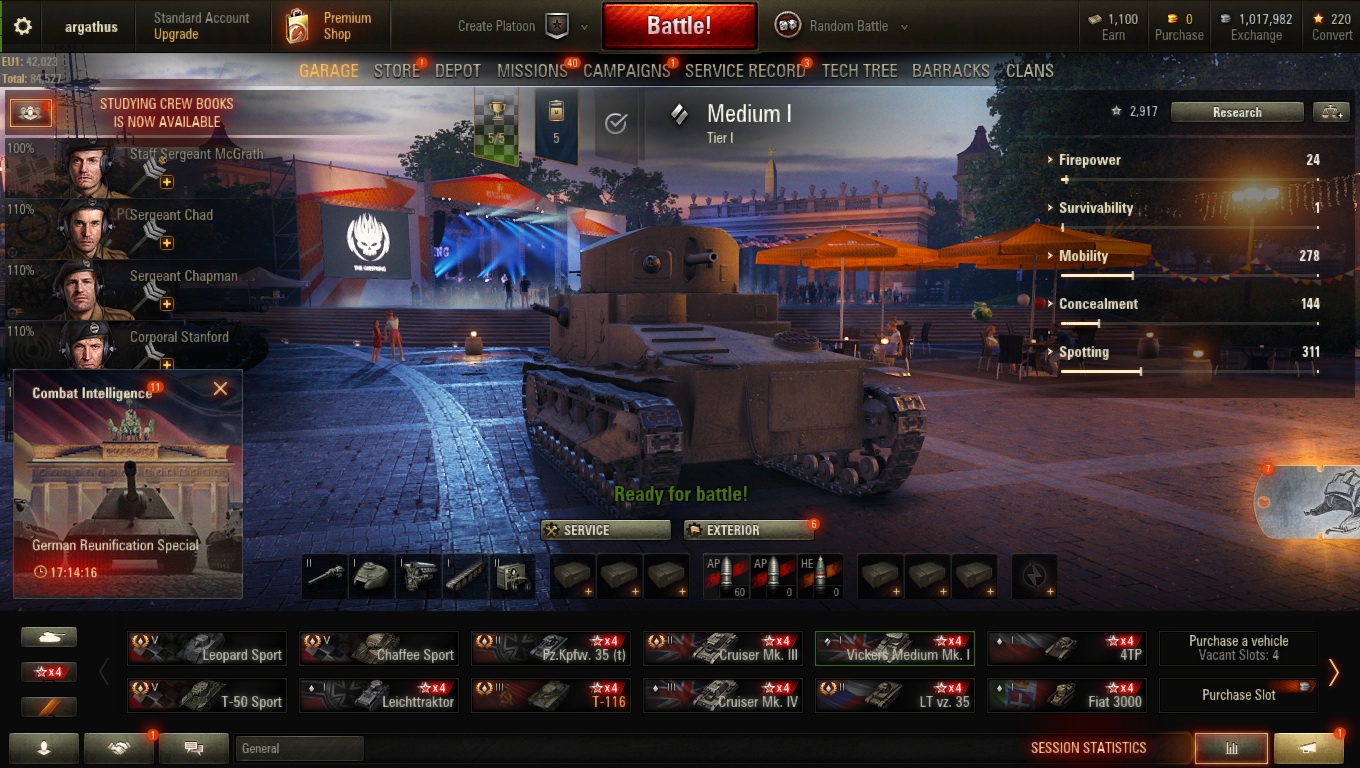
World of Tanks, 1280x1024 (5:4)
World of Tanks, 1360x768 (16:9)
Resizing and aspect ratio
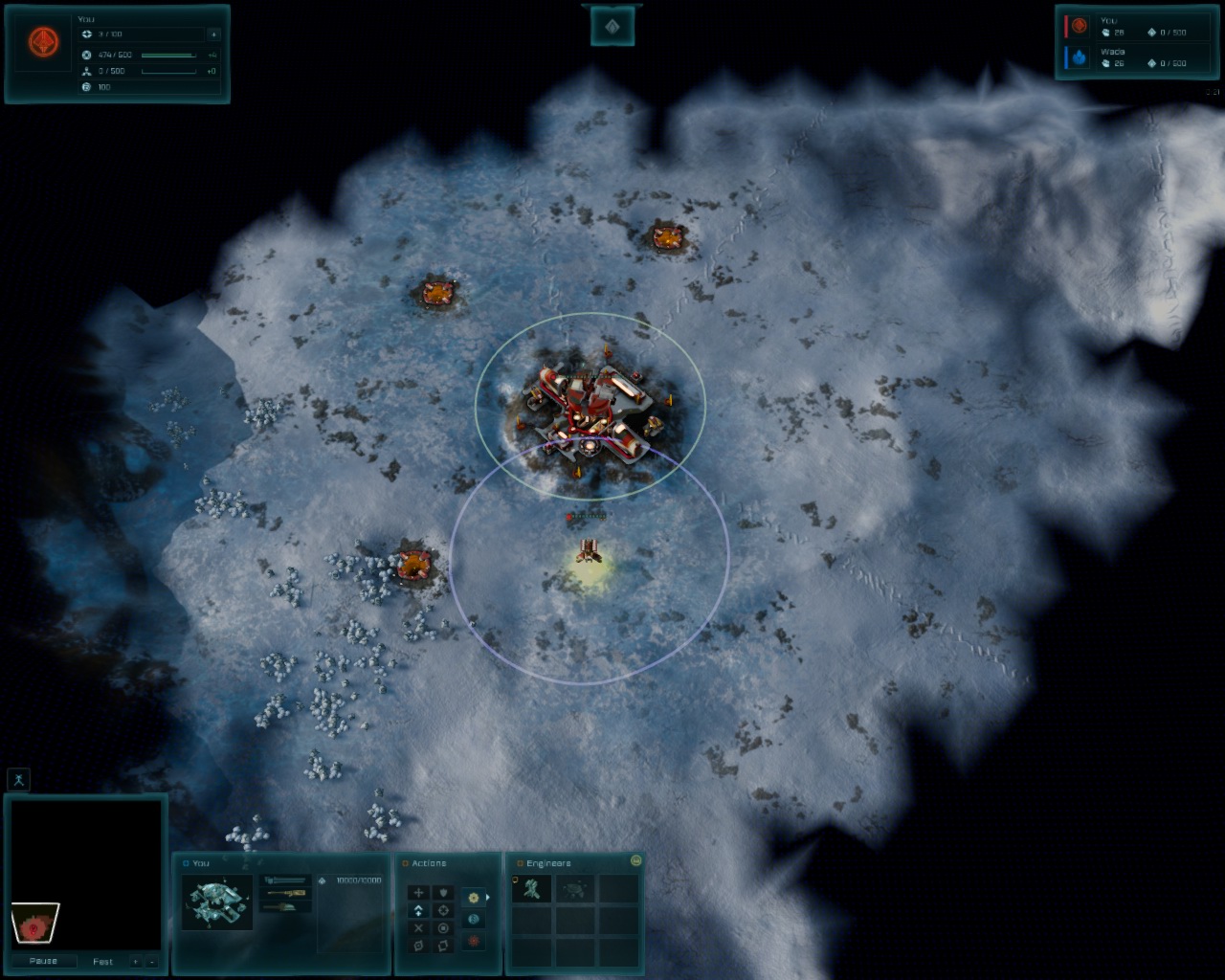
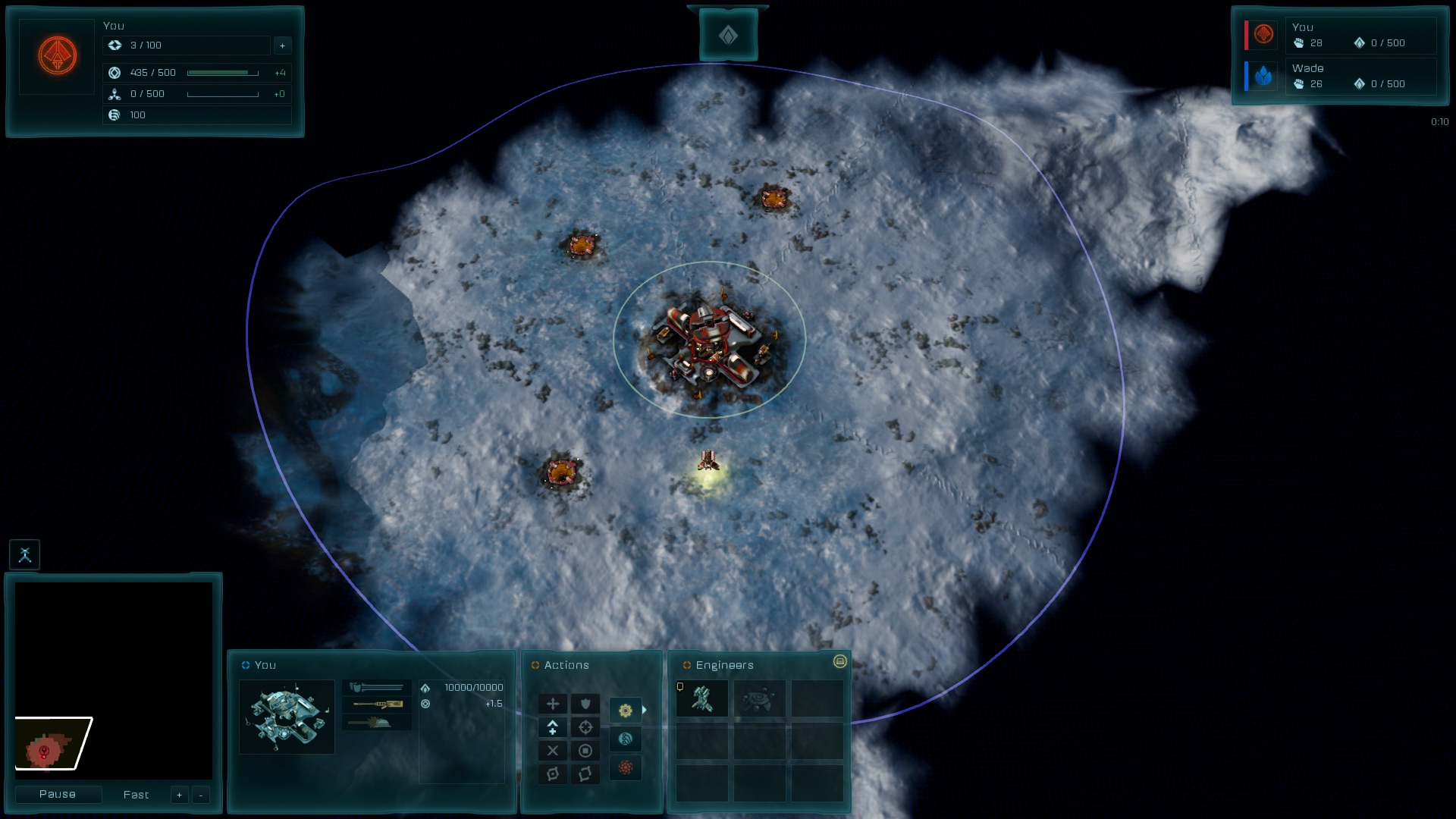
Ashes of the singularity, 1280x1024 (5:4)
Ashes of the singularity, 1920x1080 (16:9)
Resizing and aspect ratio


Hollow knight, 1280x800 zoomed (16:10)
Hollow knight, 2560x1440 zoomed (16:9)
Resizing and aspect ratio

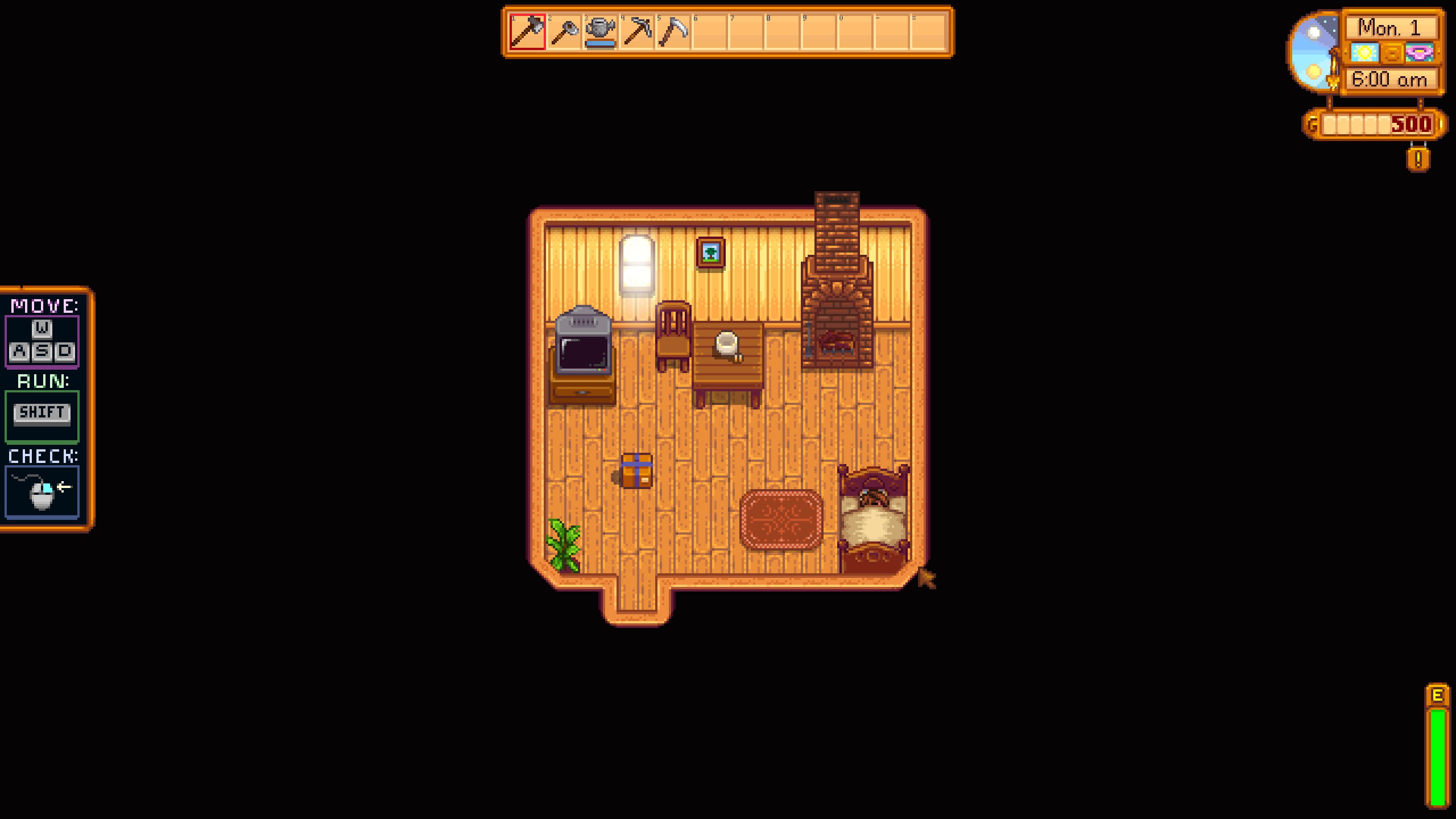
Stardew valley, 1440x900 (16:10)
Stardew valley, 2560x1440 (16:9)
Resizing and aspect ratio
- 3D games are in certain advantage -> the aspect ratio affects the camera, the resolution affects shader sampling
- 2D games tend to display all textures pixel-perfect -> textures for various resolutions
- aspect-ratio is either harcoded or it only affects the position of HUD elements
- Web games are more complicated as both the resolution and the aspect-ratio can be arbitrary
- Simple solution: fixed aspect-ratio and fixed resolution, variable scale
- by using CSS and JavaScript, we can make the canvas fill the entire screen
- Example

Display Entities
Sprite
let texture = PIXI.Texture.from("./assets/lab02/sonic.png");
this.sonic = new PIXI.Sprite(texture); // or PIXI.Sprite.from(<url>)
Primitives
- API is similar to the Canvas API (moveTo, lineTo,...)
Bitmap text
this.loader.add('myFont', './assets/lab02/dosfont.fnt').load(() => {
let text = new PIXI.BitmapText("Pixel bitmap font", { font: { name: "PxPlus IBM VGA8", size: 80 }, align: "center" });
this.stage.addChild(text);
});
Regular text
const style = new PIXI.TextStyle({ fontFamily: 'Adventure', fontSize: 36,
fill: ['#ffffff', '#00ff99'], // gradient
stroke: '#4a1850', strokeThickness: 5, });
let text = new PIXI.Text("Regular font", style);
- requires the font to be loaded via @font-face in CSS
Particles
this.container = new PIXI.ParticleContainer(DisplayParticles.particlesNum, {
position: true, // allows to change position during update
rotation: true, // allows to change rotation during update
});
- container that speeds up rendering of a high number of objects (100+)
- some attributes (masking, children, filters,...) will not work on sprites in this batch
Interactivity
// set interactivity
this.sonic.interactive = true;
// will display hand icon
this.sonic.buttonMode = true;
this.sonic.on('pointerdown', () => { this.animRunning = !this.animRunning; });
Pixel-perfect hit-test
- more of a hacky way
- overrides Sprite.containsPoint, generates a hitmap, 1 bits per pixel of baseTexture
Z-Index
- sortableChildren must be set to true for the whole subtree
- affects the order of children inside the container
Sound
- requires pixi-sound library (no Typescript types
- uses WebAudio API
Waveforms
- WebAudio API can be used separately for advanced features (synthetic sound)