Introduction to the world of games and game engines

What is a game?
What is a game?
What is a game?
What is a game?

curiosity
system
outcome
conflict
activity
endogeneous
goal
surprise
rules
disequilibrium
What is a computer game?
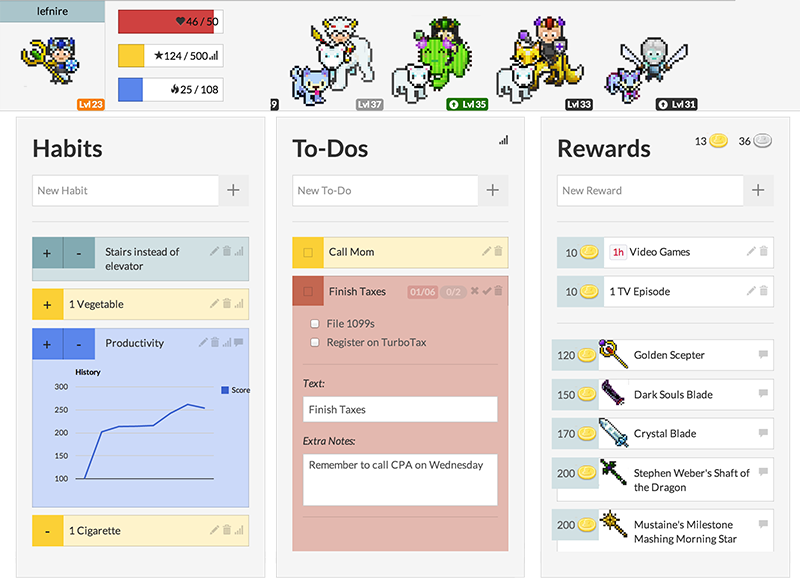
Habitica
Yet the line between them is blur.
Computer Program
- a set of instructions that can be executed by a computer
Computer Application
- computer program that helps a user to perform a task
Computer game
- a computer-controller game where players interact with objects displayed on a screen for the sake of entertainment
Computer games vs applications

Mechanics
Gameplay
Dynamics
Use-case
UX
Feedback
General consensus
Computer games are real-time interactive agent-based simulators.
List of terms
Emergence
- refers to the fact that the behavior is the result of a complex and dynamic system of rules
Progression
- refers to the structures in games where a designer outlined the possible game states beforehand, usually through level design.
Gameplay
- an emergent property of the game as defined by its rules
Mechanics
- set of rules governing the behavior of a single game element.
System
- interacting group of game elements forming a unified whole
Level
- structure in a game that dictates what challenges players encounter
Simulation
- a representation of a source system via a less complex system that correlates with the user's understanding of the source system
Topics

Game basic elements
Mechanics
- a set of rules governing the behavior of a single game element
Story
- a sequence of events that unfolds in the game
Aesthetics
- how the game looks, sounds, tastes, feels,...
Technology
- any materials and interactions that make the game possible
Mechanics
Factorio
Story

Naughty Dog games

Bethesda games

Valve games
Aesthetics

INSIDE
Technology
Spore
Example: Space Invaders
Mechanics - interesting and well-balanced
Story - didn't need to have a story
Aesthetics - three different alien designs
Technology - first videogame of it's kind
Example: Doom

Mechanics - many weapons, enemies, levels, locations,...
Story - unnamed hero (Doomguy) fighting against invading demons
Aesthetics - advanced sounds and music (for that time period)
Technology - pseudo 3D FPS perspective
Example: No man's sky

Mechanics - exploration, crafting, gathering, building
Story - space-exploration game with heavy resource-gathering elements
Aesthetics - visually stunning lush world
Technology - (pseudo)random generated world
Example: League of Legends

Mechanics - crowd, control, elo, gank, items, juking, kills, kiting, last hit, pushing, recall, points, terminology, warding, zoning
Story - a plethora of stories on LoL blog
Aesthetics - cartoonish style
Technology - MOBA (Multiplayer Online Battle Arena), Riot Servers
Example: Tormentum Dark Sorrow
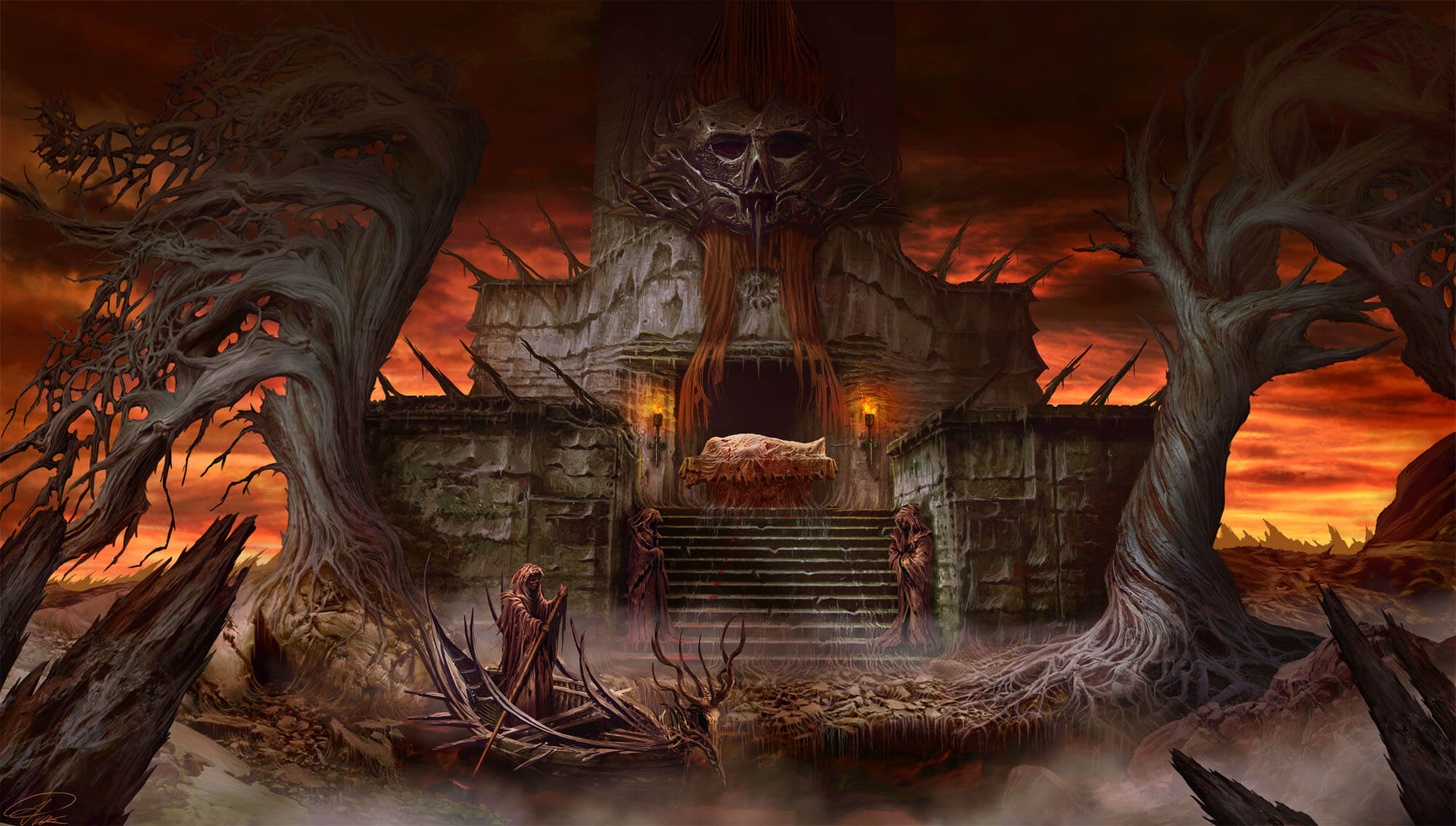

Mechanics - point-and-click adventure (go, move, examine, walk)
Story - the main element of the game
Aesthetics - biomechanic surrealism
Technology - not very ground-breaking
Game Mechanics

Space
- various spaces that can exist in a game and how they are related
Objects, attributes
- entities that can be seen or manipulated
Actions
- an object's turn to act
Rules
- statements that describe constraints, consequences and goals
Example: Pong

Space - 2D board
Objects - two players (paddles) and colliding ball, score
Actions - move up/down (1 degree of freedom), release the ball
Rules - the ball has a constant linear velocity. Angle of incidence is angle of reflection. Player earns one point when the other player fails to return the ball. The winner is the one who reaches eleven points before the opponent
Example: Tronic
What is a game engine?
PRE-engine era




1984: Breakout for DOS
move_paddle
;read input from joystick
lda joystick2;joy port 2
and #8 ;right
beq move_paddle_right
lda joystick2
and #4 ;#left
beq move_paddle_left
rts
check_ball_paddle_collision
lda sprite_collision
and #2
cmp #2
beq ball_paddle_collision
rts
ball_paddle_collision
lda sprite_collision
and #2
sta sprite_collision ;clear cbit
jsr set_ball_direction_up
rts
1989: Prince of Persia
Prince of Persia guard controller
:underctrl
lda CharSword
cmp #2 ;in fighting mode?
beq FightCtrl ;yes
lda CharID
cmp #2 ;kid or shadowman?
bcc :cont
jmp GuardCtrl ;no
* What is he doing now?
:cont ldx CharPosn ;previous frame #

Source code: link
ID Tech
- Family of game engines developed by ID software
- Id Tech 0 - the very first engine
- Every next game had more advanced technology
- Still, memory constraints sabotaged attempts to create data-heavy design

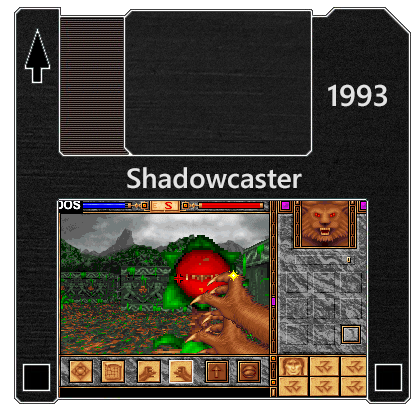
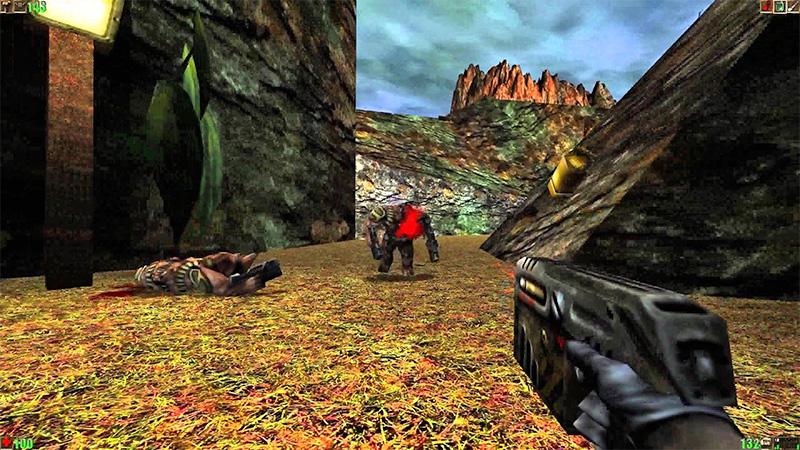
1993: DOOM
boolean P_CheckMissileRange (mobj_t* actor){
if (!P_CheckSight(actor, actor->target))
return false; // can’t see the target
if ( actor->flags & MF_JUSTHIT ) {
// just hit -> fight back!
actor->flags &= ~MF_JUSTHIT;
return true;
}
if (actor->reactiontime)
return false; // do not attack yet
dist = P_AproxDistance (actor, target)
- 64*FRACUNIT;
// no melee attack, so fire more
if (!actor->info->meleestate)
dist -= 128*FRACUNIT;
// check for ARCH-VILE
if (actor->type == MT_VILE){
if (dist > 14*64)
return false; // too far away
}
}
WAD File
"Where's All the Data?"
- Binary format of package files for Doom
- Levels (walls, floors, monsters)
- Sound effects, music
- Color palettes, images
- Designed by John D. Carmack

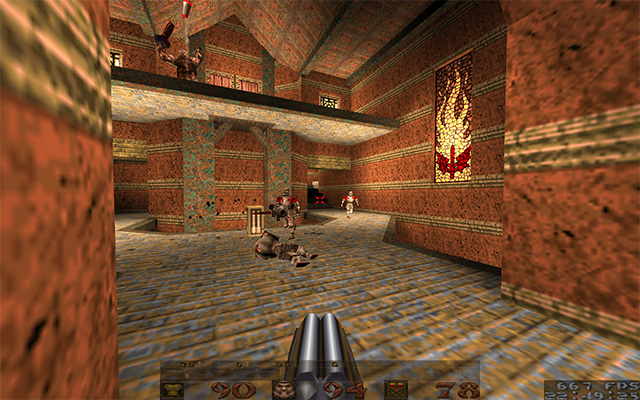
1996: Quake
void() DeathSound = {
local float rs;
// water death sounds
if (self.waterlevel == 3) {
DeathBubbles(5);
sound (self, CHAN_VOICE,
"player/h2odeath.wav", 1, ATTN_NONE);
return;
}
rs = rint ((random() * 4) + 1);
if (rs == 1)
self.noise = "player/death1.wav";
if (rs == 2)
self.noise = "player/death2.wav";
if (rs == 3)
self.noise = "player/death3.wav";
if (rs == 4)
self.noise = "player/death4.wav";
if (rs == 5)
self.noise = "player/death5.wav";
sound (self, CHAN_VOICE, self.noise, 1, ATTN_NONE);
return;
};
Quake Engine
- ~id Tech 1
- Released by id Software in 1996
- True 3D real-time rendering
- Binary space partitioning
- 3D light sources, Gouraud shading
- Games released: Quake, Hexen 2, Silver Wings
- Source code released in 1999
Successors:
- id Tech 2: 1997
- id Tech 3: 1999
- id Tech 4: 2004
- id Tech 5: 2011
- id Tech 6: 2016
- id Tech 7: 2018 (Doom Eternal)

Unreal Engine

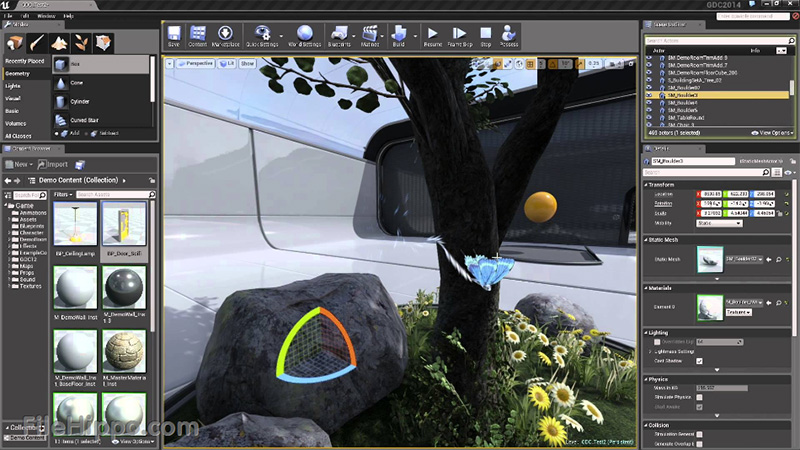


Unreal Engine 1
- Released in 1998 by Epic Games as FPS game engine
- Unreal - the first game powered by this engine
- Concept of assets, HW & SW rendering, collision detection,...
Unreal Engine 4
- Robust multiplayer framework
- Film-Quality postprocessing
- VFX & Particle systems
- Beta Raytracing
CryEngine


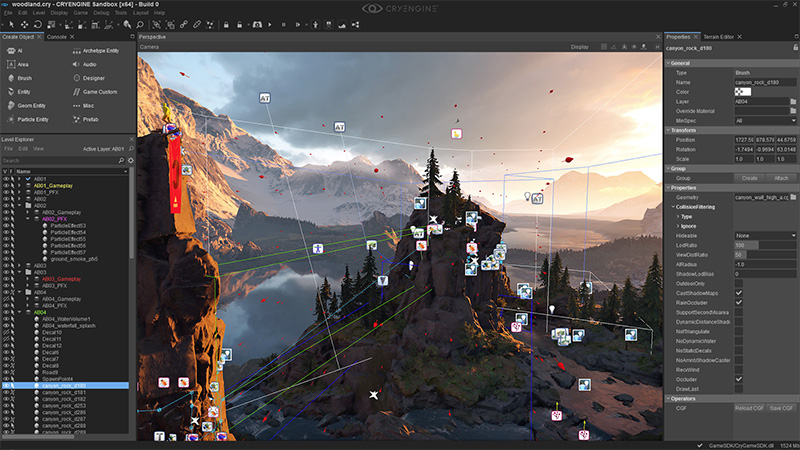

- Released in 2002 as a technology demo for NVidia
- Far Cry - the first game powered by CryEngine
- Pushes hardware to its absolute limits
CryEngine V - current release
- Dynamic global illumination
- Destructible environment
- AI editing system
Unity



- All-purpose (not only) game engine
- First announced for MacOS in 2005
- over 27 platforms supported
- Best choice for indie developers
Unity 2019.2 - current version
- DirectX, OpenGL, Vulkan
- 2D and 3D games
Evolution of Games
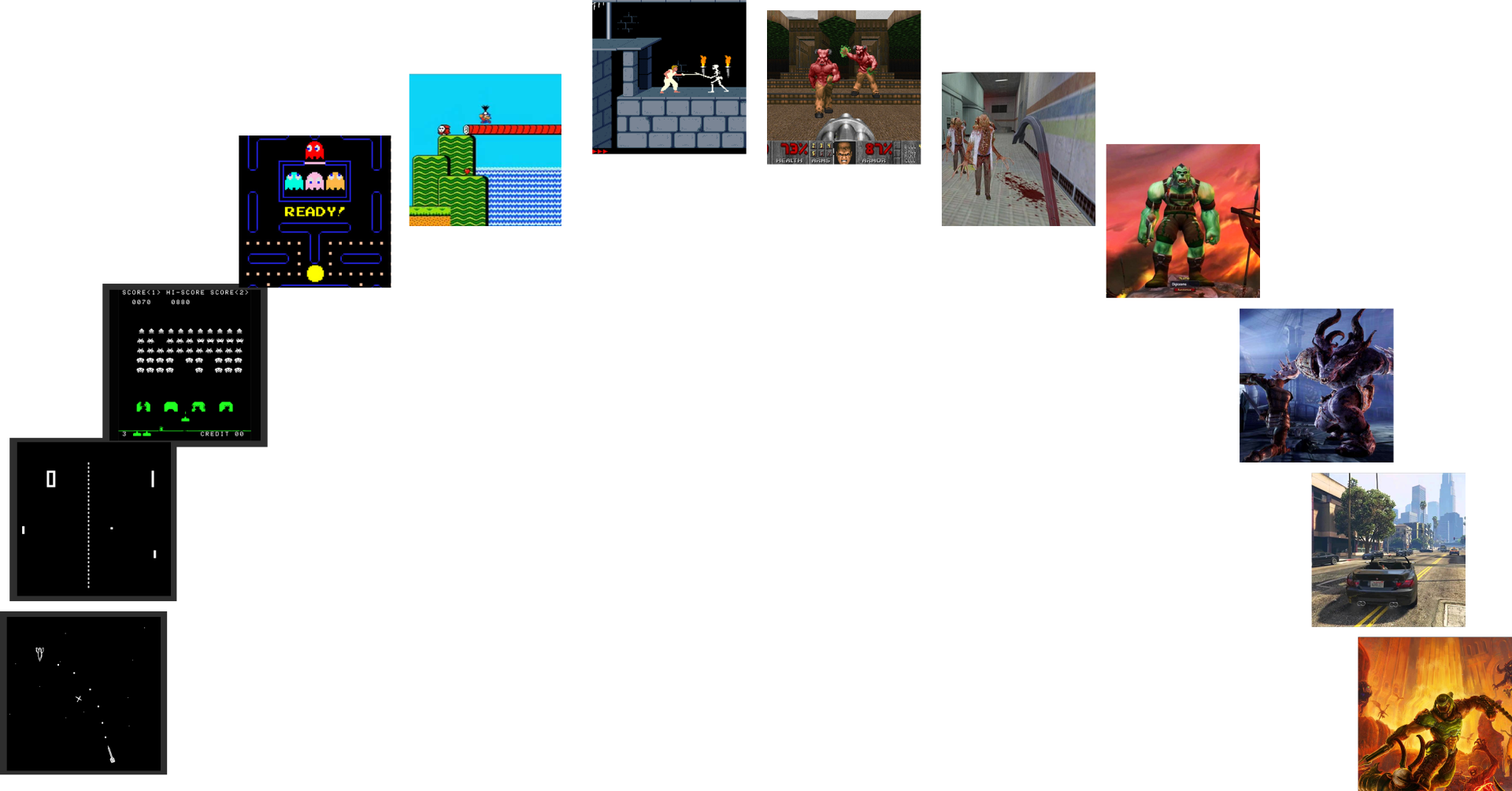
Evolution of Games

Game Engines Today

Important note
A game engine is just a tool, nothing more. Game development is more about dedication, enthusiasm and ability to work very hard.
Lecture 1 Review
Terms:
- Gameplay
- Mechanics
- System
- Level
- Emergence
- Progression
- Simulation
Computer games are real-time interactive agent-based simulators
Game Basic Elements: Mechanics, Story, Aesthetics, Technology
Game Mechanics: Space, Objects and Attributes, Actions, Rules
Goodbye quote
So you walk eternally through the shadow realms, standing against evil where all others falter. May your thirst for retribution never quench, may the blood on your sword never dry, and may we never need you again.Doom 4